Power Quality Analysis
Power Quality and Reliability is the key to the successful delivery of quality product and uninterrupted operation of industry, be it conventional or service sector. It is now even more critical to the industry, pursuing Energy Efficiency (EE) because of the increasing application of electronic loads and digital controllers which are sensitive to the quality of power supplied. These can have serious economic consequences and cost business millions of rupees each year in revenue loss, process improvements, opportunity loss, equipment failure, electrical hazards like fire and scrapped product. Any such incident reflects adversely in specific energy consumption (SEC) by an industry.
The world has changed. We are no more in pure sine wave era controlled by linear loads; rather we are almost fully controlled by non-linear loads. In the world of power electronics, bad power quality phenomenon can cause malfunctioning of sophisticated equipment.
Disturbances which are likely to disturb the correct operation of industrial equipment and processes is generally ranked in various classes relating to conducted and radiated disturbance:
- low frequency (< 9 kHz),
- high frequency (u 9 kHz),
- electrostatic discharge.
Measurement of PQ usually involves characterizing low frequency conducted electromagnetic disturbances (the range is widened to include transient overvoltage’s and transmission of signals on a power system):
- voltage dips and interruptions
- harmonics and interharmonics
- temporary overvoltages
- swell
- transient overvoltages
- voltage fluctuations
- voltage unbalance
- power-frequency variations
- DC in AC networks
- Signalling voltages
It is not generally necessary to measure each type of disturbance. The types can be placed in four categories, affecting the magnitude, waveform, frequency and symmetry of the voltage. Several of these characteristics may be modified simultaneously by any one type of disturbance. Disturbances can also be classified according to their permanent, semi-permanent or random nature (lightning, short-circuit, switching operations, etc.).
What is Power Quality Analysis?
General:
The Power Quality Audit (PQA), is a service offered by our expert engineers that checks the reliability, efficiency and safety of an organisation’s electrical system.
It verifies the following aspects:
- The continuity of the power supply: i.e., that the power in the network is available on a regular basis and is able to ensure the efficient operation of the equipment
- The quality of the voltage: i.e., that there are no low or high frequency disturbances in the network capable of damaging the system components.
The PQA uses network analyzers, instruments specially designed to detect faults and deteriorations and record parameters and information that may be of use in locating the causes of disturbances. The data is collected and analyzed by our engineers, who can then diagnose the problems and suggest the most appropriate solutions.
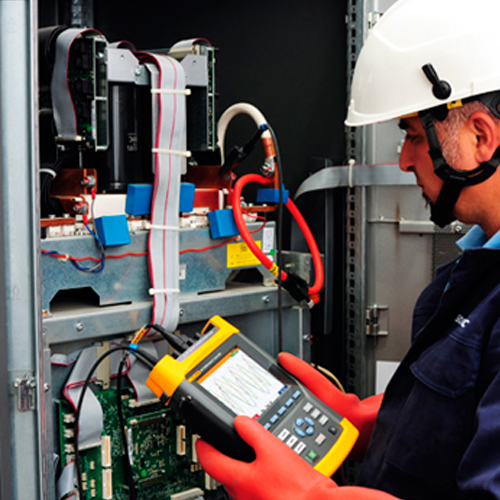

What does the ‘quality’ of power mean?
A quality electrical power supply must be available at all times, always within the frequency and magnitude tolerance limits, and always with a perfectly sinusoidal waveform.
A reliable, efficient and safe power supply is essential for guaranteeing productivity and precision in any organisation. Business and industrial organisations, public authorities, hospitals and laboratories and banking and finance groups are relying more and more on computerised and electronic equipment for their daily work activities. These important electrical loads are subject to a range of disturbances that adversely affect the quality of the power supply and the reliability of the electrical system.
Power Quality Category:
Harmonic-distortion
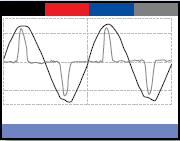
Most distortion is attributable to the third harmonic, typical of IT equipment
Imbalance on three-phase load
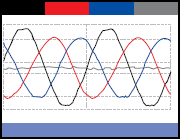
Imbalances are typical in organization’s that keep adding new loads to systems
Voltage dips/drop and flicker
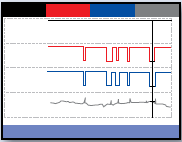
Transitory currents constitute almost 90 % of electrical disturbances
Reduction of power factor
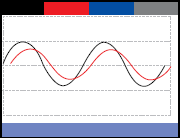
Sometimes, the cost of remedying the reduced power factor problem is much less than the payment of a penalty charge
Transitory current_over voltage
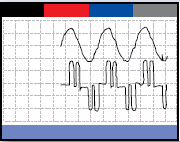
Transitory currents are harder to detect without a specific
The Risks:
Ignoring the symptoms of possible disturbances in the electrical system could lead to damaged equipment, consequently reducing its working efficiency and shortening the life span. The resulting break in critical processes (i.e. machine downtime) could lead to a loss of earnings that could far outweigh the mere cost of the actual operation. In addition, there is also the likely risk of having to bear increased energy costs and pay penalty charges in electricity bills, with the possibility of legal disputes with energy providers.
PQA Improvement Measures:
The quality of the energy can be improved by taking action on 3 levels:
- User’s electrical system
- Equipment connected to system
- Main Grid Supply

If the problem is in the electrical system, the PQA could advise the user to install active or passive filters, harmonic compensators, emergency generators or UPS systems, or to intervene directly on the system structure (transformers, new distribution lines, etc.).
Although the advance of technology has led to the introduction of standards that tend to reduce the creation of disturbances and make equipment less disturbance-prone, problems can however arise with the mismatching of non-homogeneous equipment in the same system. The PQA makes it possible to find the right arrangement within the system. If the problem lies in the source, or electricity mains, the PQA may encourage the customer to contact the provider in order to improve the supply contract parameters.
Advantages of Effective PQA:
The PQA final report provides a complete picture of the electrical system’s correct state of operation. The report is a tool of primary importance for preventive maintenance, in that it lists all the measures to be taken promptly when disturbances are detected, before the negative impact on production and the running of the equipment is felt.



